AI is essentially becoming central to product development across industries. For today’s product managers, this shift is as transformative as the move to mobile or cloud computing was a decade ago. Those who embrace AI will gain a significant edge, while those who resist risk being left behind.
If you’re looking to future-proof your career, now is the time to understand what it means to be an AI product manager, what skills you need, and how to develop a clear AI product manager roadmap for 2025 and beyond.
Key Takeaways
- AI is becoming an essential skill for product managers to stay competitive in 2025 and beyond.
- A clear AI product manager roadmap helps identify opportunities, align with goals, deploy effectively, and iterate.
- Strong collaboration across technical, design, and compliance teams is crucial for AI product success.
- Ethical considerations and bias management must be addressed from the start to ensure fair and trustworthy AI solutions.
Who Is an AI Product Manager?
An AI product manager isn’t a completely new role, it’s the evolution of the traditional product manager. The core responsibilities remain the same: aligning product strategy with business goals, delivering customer value, and collaborating across teams.
The difference lies in their ability to leverage AI technologies effectively. Just like the introduction of mobile or cloud demanded new skills from PMs, AI requires a deep understanding of machine learning capabilities, ethical considerations, and data-driven product design.
As one industry expert puts it:
“AI won’t replace product managers, but product managers who fail to embrace AI will be replaced by those who do.”
Why AI Is Different From Traditional Software
AI products do more than just execute pre-programmed instructions. They learn, adapt, and improve over time. This creates unique opportunities and challenges for PMs.
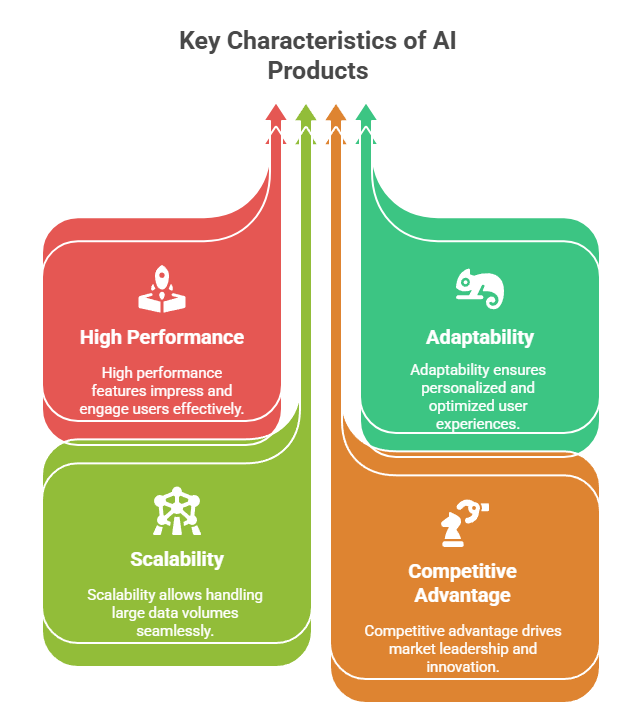
Key characteristics of AI products include:
- High Performance: Features that “wow” users, like Netflix’s personalized recommendations or ChatGPT’s conversational abilities.
- Adaptability: AI systems continuously learn and optimize, delivering more personalized experiences.
- Scalability: The ability to handle vast amounts of data effortlessly.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies like Amazon, Spotify, and Tesla leverage AI for logistics, personalization, and real-time decision-making.
AI in Product Management: Beyond the Product
AI makes products smarter, and it also transforms workflows. Here are a few practical applications:
- Session Replays at Scale: Tools like FullStory analyze user interactions to uncover usability issues quickly.
- Turning Feedback into Features: Sentiment analysis platforms identify the most impactful features to prioritize.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Analytics platforms like Amplitude democratize insights, helping PMs make faster, evidence-based choices.
Whether you’re optimizing Uber’s dynamic pricing or Duolingo’s lesson personalization, AI can streamline decision-making and boost customer satisfaction.
Also Read: How to Become AI Product Manager: Insights from Industry Expert
The AI Product Manager Strategy
As an AI Product Manager, you act as a bridge between AI technology and real-world customer value. Below is a step-by-step framework based on industry best practices and examples from leading companies.
Step 1: Identify High-Impact AI Use Cases
The first responsibility of an AI product manager is to pinpoint where AI can add tangible value. Not every problem needs AI; sometimes, a rules-based system is enough. Your goal is to find problems where AI offers a competitive edge, scalability, or personalization that traditional approaches cannot.
How to approach it:
- Audit your current product workflows and user journeys to identify friction points.
- Look for areas with large, rich datasets—AI thrives where data volume and complexity are high.
- Validate the potential ROI by estimating business impact (e.g., revenue increase, cost savings, customer retention).
Examples:
- Expedia: Uses AI to dynamically price travel insurance, helping customers during emergencies while optimizing margins.
- H&M: Predicts fashion trends months in advance using AI, reducing overstock and increasing sell-through rates.
- Healthcare apps: Predict patient readmissions and suggest preventive measures, improving outcomes and reducing hospital costs.
Step 2: Align AI Capabilities with Business Objectives
Even the most advanced AI features will fail if they don’t align with your company’s strategic priorities. This means translating AI capabilities into clear business and user benefits.
Key questions to ask:
- Does this AI feature solve a business-critical problem?
- How will it improve key metrics like customer satisfaction, retention, or revenue?
- Is there a clear user story that explains the value of AI?
Examples:
- Microsoft: Saves millions annually by using AI to translate technical documentation into 100+ languages, improving accessibility and reducing manual translation costs.
- Spotify: Analyzes listening habits to create Discover Weekly, improving engagement and reducing churn.
- Salesforce Einstein: Recommends the “next best action” to sales reps, directly influencing deal closures and revenue growth.
Step 3: Build a Cross-Functional AI Delivery Plan
An AI product manager’s role is not to build the model themselves, but to coordinate the ecosystem, from data engineers and ML scientists to designers and compliance teams.
Responsibilities include:
- Collaborating with data scientists to ensure the model is trained on clean, representative datasets.
- Working with UX designers to create user experiences that make AI outputs understandable and trustworthy.
- Coordinating with legal and compliance teams on privacy, security, and ethical standards.
Examples:
- A fintech PM works with ML teams to create an AI-based fraud detection system, then with designers to ensure alerts are clear and actionable for non-technical customer service reps.
- A retail PM partners with AI engineers to predict demand, and with operations teams to align inventory levels.

Step 4: Oversee Model Deployment and Monitoring
Launching an AI feature is not the finish line, it’s the starting point for ongoing improvement.
Your focus here should be:
- Performance monitoring: Track model accuracy, latency, and reliability in real-world conditions.
- User feedback loops: Collect qualitative and quantitative feedback to spot issues early.
- Ethics and fairness checks: Continually validate that the model’s outputs are unbiased and compliant.
Examples:
- Customer support automation: A company replaces its first-level helpdesk with an AI chatbot trained on product documentation. The PM sets up KPIs like resolution rate, customer satisfaction scores, and fallback-to-human frequency to monitor success.
- Accessibility AI: Microsoft’s Vision AI integrates with ethical guidelines to assist visually impaired users, showing how AI deployment can align with social responsibility.
Step 5: Balance Cost, Feasibility, and Ethics
Every AI initiative faces trade-offs. As the AI product manager, you’ll need to decide whether to build, buy, or partner, and ensure that the chosen solution is sustainable.
Considerations:
- Build: More control but higher upfront cost and time-to-market.
- Buy: Faster to deploy, but limited customization.
- Partner: Shares risk but may involve dependency on external parties.
Ethical aspects include:
- Avoiding “black-box” AI, where results can’t be explained to stakeholders.
- Mitigating bias in datasets to ensure fair and inclusive outcomes.
- Complying with regulations like GDPR or CCPA for data privacy.
Step 6: Create a Continuous Learning Culture
Unfortunately, AI models decay over time, trends shift, and user expectations evolve. An AI product manager must foster a culture of ongoing iteration.
Action points:
- Schedule regular model retraining cycles.
- Run A/B tests on new AI features.
- Invest in your own upskilling to stay ahead on emerging AI tools, regulations, and ethical debates.
✅ In summary, your AI product manager roadmap for 2025 should look like this:
- Identify high-impact AI opportunities.
- Align them with business objectives.
- Coordinate cross-functional delivery.
- Deploy, monitor, and refine AI features.
- Balance cost, feasibility, and ethics.
- Keep learning and iterating.
Essential Skills for an AI Product Manager
To succeed, focus on developing these core skills:
- AI Product Sense: Recognizing where AI can drive the most value.
- Data Literacy: Ensuring clean, unbiased, and high-quality data for model training.
- UX Design for AI: Creating adaptable and ethical user experiences.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Bridging the gap between technical and non-technical teams.
- Bias Mitigation: Actively addressing and minimizing bias in both training data and AI outputs.
Also Read: Top 6 AI Product Management Skills for Success in 2024
Conclusion
AI is a defining capability that will separate tomorrow’s leaders from the rest. By following a clear AI product manager roadmap, you can not only harness the power of AI to build smarter, more personalized products but also shape the strategic direction of your organization in an AI-first world.
The key is to start now and embrace AI’s potential, navigate its challenges with ethics and responsibility, and continually evolve your skills.
FAQs – AI Product Manager Roadmap
1. What does an AI product manager do?
An AI product manager oversees the development and deployment of AI-powered features, ensuring they align with business objectives, deliver customer value, and meet ethical standards.
2. How is an AI product manager different from a regular product manager?
While both roles focus on product strategy and delivery, an AI PM specializes in integrating AI capabilities, managing data-driven features, and addressing the unique challenges of AI development.
3. What skills are essential for AI product managers?
Core skills include AI product sense, data literacy, UX design for AI, cross-functional collaboration, and bias mitigation.
4. How can I become an AI product manager?
Start by learning AI fundamentals, advocating for AI projects in your current role, gaining hands-on experience, and pursuing targeted certifications or training programs.












